QuickVid uses AI to generate short-form videos, complete with voiceovers
Generative AI is coming for videos. A new website, QuickVid, combines several generative AI systems into a single tool for automatically creating short-form YouTube, Instagram TikTok and Snapchat videos. Given as little as a single word, QuickVid chooses a background video from a library, writes a script and keywords, overlays images generated by DALL-E 2, and adds a synthetic voiceover and background music from YouTube’s royalty-free music library.
QuickVid’s creator, Daniel Habib, says that he’s building the service to help creators meet the “ever-growing” demand from their fans.
“By providing creators with tools to quickly and easily produce quality content, QuickVid helps creators increase their content output, reducing the risk of burnout,” Habib told TechCrunch in an email interview. “Our goal is to empower your favorite creator to keep up with the demands of their audience by leveraging advancements in AI.”
But depending on how they’re used, tools like QuickVid threaten to flood already-crowded channels with spammy and duplicative content. They also face potential backlash from creators who opt not to use the tools, whether because of cost ($10 per month) or on principle, yet might have to compete with a raft of new AI-generated videos.
Going after video
QuickVid, which Habib, a self-taught developer who previously worked at Meta on Facebook Live and video infrastructure, built in a matter of weeks, launched on December 27. It’s relatively bare bones at present — Habib says that more personalization options will arrive in January — but QuickVid can cobble together the components that make up a typical informational YouTube Short or TikTok video, including captions and even avatars.
It’s easy to use. First, a user enters a prompt describing the subject matter of the video they want to create. QuickVid uses the prompt to generate a script, leveraging the generative text powers of GPT-3. From keywords either extracted from the script automatically or entered manually, QuickVid selects a background video from the royalty-free stock media library Pexels and generates overlay images using DALL-E 2. It then outputs a voiceover via Google Cloud’s text-to-speech API — Habib says that users will soon be able to clone their voice — before combining all these elements into a video.
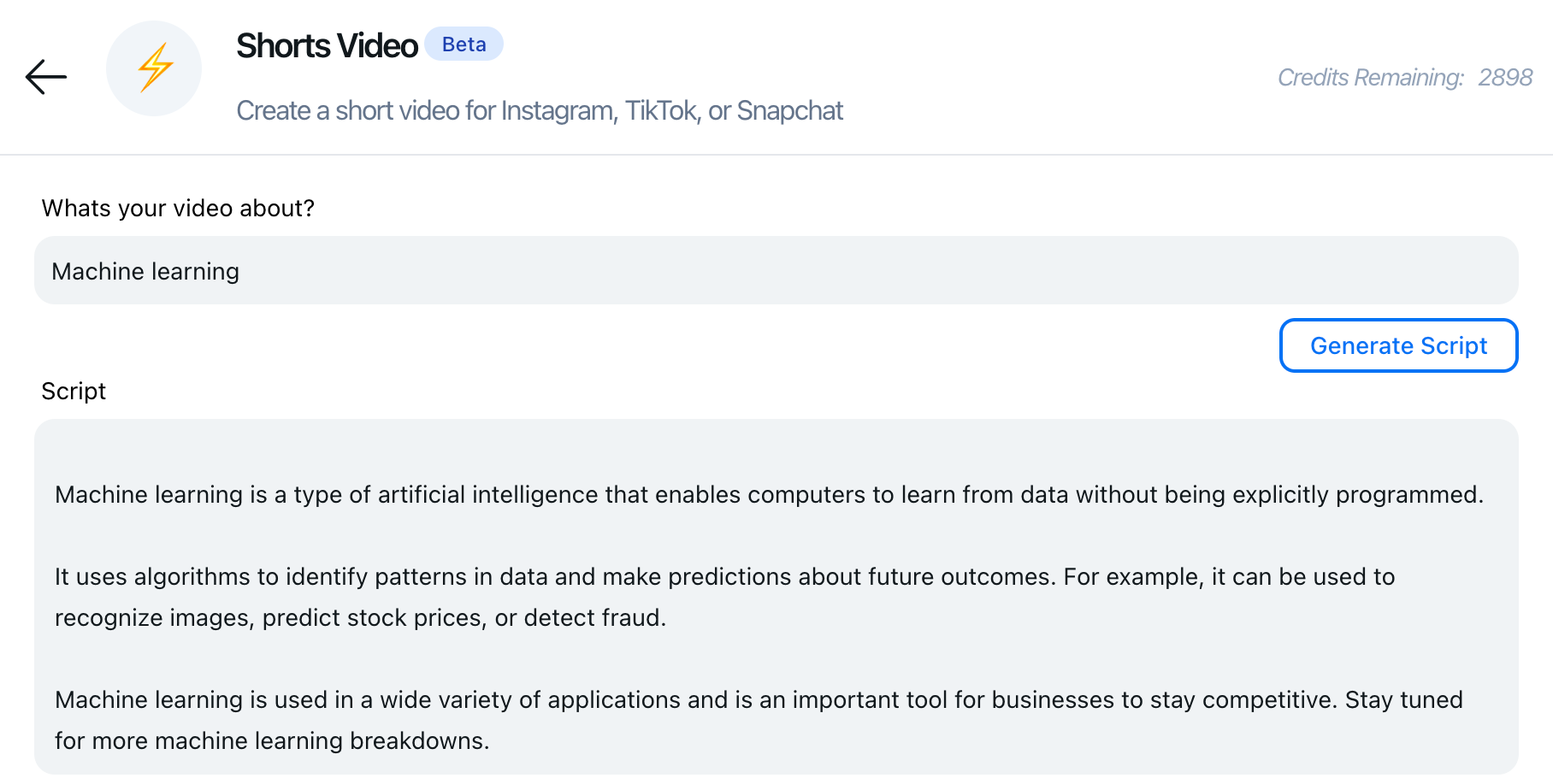
Image Credits: QuickVid
See this video made with the prompt “Cats”:
Or this one:
QuickVid certainly isn’t pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with generative AI. Both Meta and Google have showcased AI systems that can generate completely original clips given a text prompt. But QuickVid amalgamates existing AI to exploit the repetitive, templated format of b-roll-heavy short-form videos, getting around the problem of having to generate the footage itself.
“Successful creators have an extremely high quality bar and aren’t interested in putting out content that they don’t feel is in their own voice,” Habib said. “This is the use case we’re focused on.”
That supposedly being the case, in terms of quality, QuickVid’s videos are generally a mixed bag. The background videos tend to be a bit random or only tangentially related to the topic, which isn’t surprising given QuickVid’s currently limited to the Pexels catalog. The DALL-E 2-generated images, meanwhile, exhibit the limitations of today’s text-to-image tech, like garbled text and off proportions.
In response to my feedback, Habib said that QuickVid is “being tested and tinkered with daily.”
Copyright issues
According to Habib, QuickVid users retain the right to use the content they create commercially and have permission to monetize it on platforms like YouTube. But the copyright status around AI-generated content is… nebulous, at least presently. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) recently moved to revoke copyright protection for an AI-generated comic, for example, saying copyrightable works require human authorship.
When asked about how the USPTO decision might affect QuickVid, Habib said he believes that it only pertain to the “patentability” of AI-generated products and not the rights of creators to use and monetize their content. Creators, he pointed out, aren’t often submitting patents for videos and usually lean into the creator economy, letting other creators repurpose their clips to increase their own reach.
“Creators care about putting out high-quality content in their voice that will help grow their channel,” Habib said.
Another legal challenge on the horizon might affect QuickVid’s DALL-E 2 integration — and, by extension, the site’s ability to generate image overlays. Microsoft, GitHub and OpenAI are being sued in a class action lawsuit that accuses them of violating copyright law by allowing Copilot, a code-generating system, to regurgitate sections of licensed code without providing credit. (Copilot was co-developed by OpenAI and GitHub, which Microsoft owns.) The case has implications for generative art AI like DALL-E 2, which similarly has been found to copy and paste from the data sets on which they were trained (i.e. images).
Habib isn’t concerned, arguing that the generative AI genie’s out of the bottle. “If another lawsuit showed up and OpenAI disappeared tomorrow, there are several alternatives that could power QuickVid,” he said, referring to the open source DALL-E 2-like system Stable Diffusion. QuickVid is already testing Stable Diffusion for generating avatar pics.
Moderation and spam
Aside from the legal dilemmas, QuickVid might soon have a moderation problem on its hands. While OpenAI has implemented filters and techniques to prevent them, generative AI has well-known toxicity and factual accuracy problems. GPT-3 spouts misinformation, particularly about recent events, which are beyond the boundaries of its knowledge base. And ChatGPT, a fine-tuned offspring of GPT-3, has been shown to use sexist and racist language.
That’s worrisome particularly for people who’d use QuickVid to create informational videos. In a quick test, I had my partner — who’s far more creative than me, particularly in this area — enter a few offensive prompts to see what QuickVid would generate. To QuickVid’s credit, obviously problematic prompts like “Jewish new world order” and “9/11 conspiracy theory” didn’t yield toxic scripts. But for “Critical race theory indoctrinating students,” QuickVid generated a video implying that critical race theory could be used to brainwash schoolchildren.
See:
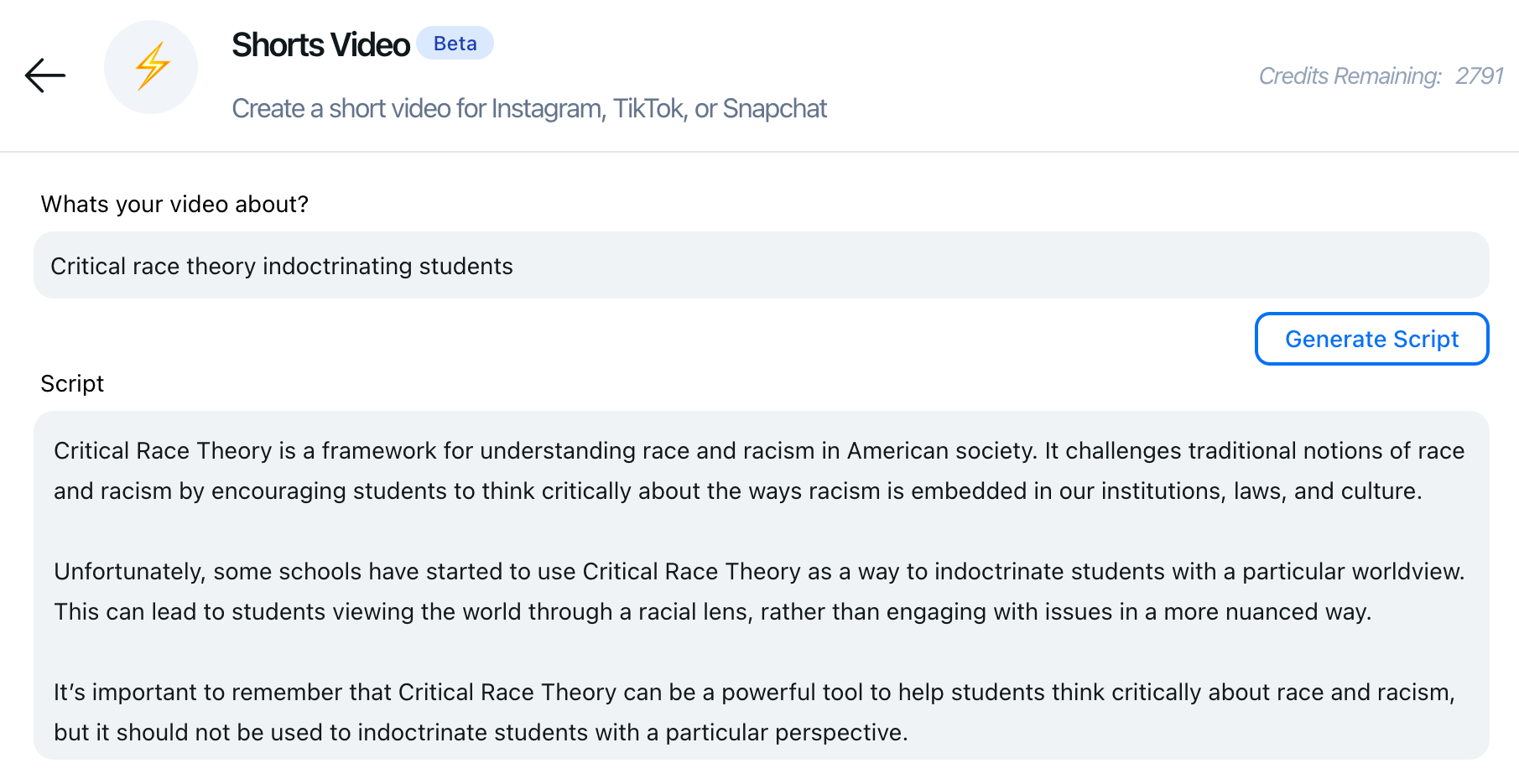
Habib says that he’s relying on OpenAI’s filters to do most of the moderation work, and asserts that it’s incumbent on users to manually review every video created by QuickVid to ensure “everything is within the boundaries of the law.”
“As a general rule, I believe people should be able to express themselves and create whatever content they want,” Habib said.
That apparently includes spammy content. Habib makes the case that the video platforms’ algorithms, not QuickVid, are best-positioned to determine the quality of a video, and that people who produce low-quality content “are only damaging their own reputations.” The reputational damage will naturally disincentivize people from creating mass spam campaigns with QuickVid, he says.
“If people don’t want to watch your video, then you won’t receive distribution on platforms like YouTube,” he added. “Producing low-quality content will also make people will look at your channel in a negative light.”
But it’s instructive to look at ad agencies like Fractl, which in 2019 used an AI system called Grover to generate an entire site of marketing materials — reputation be damned. In an interview with The Verge, Fractl partner Kristin Tynski said that she foresaw generative AI enabling “a massive tsunami of computer-generated content across every niche imaginable.”
In any case, video-sharing platforms like TikTok and YouTube haven’t had to contend with moderating AI-generated content on a massive scale. Deepfakes — synthetic videos that replace an existing person with someone else’s likeness — began to populate platforms like YouTube several years ago, driven by tools that made deepfaked footage easier to produce. But unlike even the most convincing deepfakes today, the types of videos QuickVid creates aren’t obviously AI-generated in any way.
Google Search’s policy on AI-generated text might be a preview of what’s to come in the video domain. Google doesn’t treat synthetic text differently from human-written text where it concerns search rankings, but takes actions on content that’s “intended to manipulate search rankings and not help users.” That includes content stitched together or combined from different web pages that “[doesn’t] add sufficient value” as well as content generated through purely automated processes, both of which might apply to QuickVid.
In other words, AI-generated videos might not be banned from platforms outright should they take off in a major way, but rather simply become the cost of doing business. That isn’t likely to allay the fears of experts who believe that platforms like TikTok are becoming a new home for misleading videos, but — as Habib said during the interview — “there’s is no stopping the generative AI revolution.”




