Turkey’s Anatolian Fault Rivals California’s San Andreas
Californians may be very familiar with the San Andreas Fault, but it turns out that Türkiye has one of its own that rivals the Western United States
‘ rift. In fact, the Anatolian Fault is much longer and deeper than the San Andreas Fault, and it comes very close to a highly populated city.
Here’s what to know about the Anatolian Fault in Turkey, and how it stacks up against the San Andreas Fault, which runs through California
.

Related
Is The West Coast Really Going To Fall Into The Ocean?
Will California and other West Coast states drop into the ocean one day?
The Anatolian Fault Is As Deep As 62 Miles In Some Places
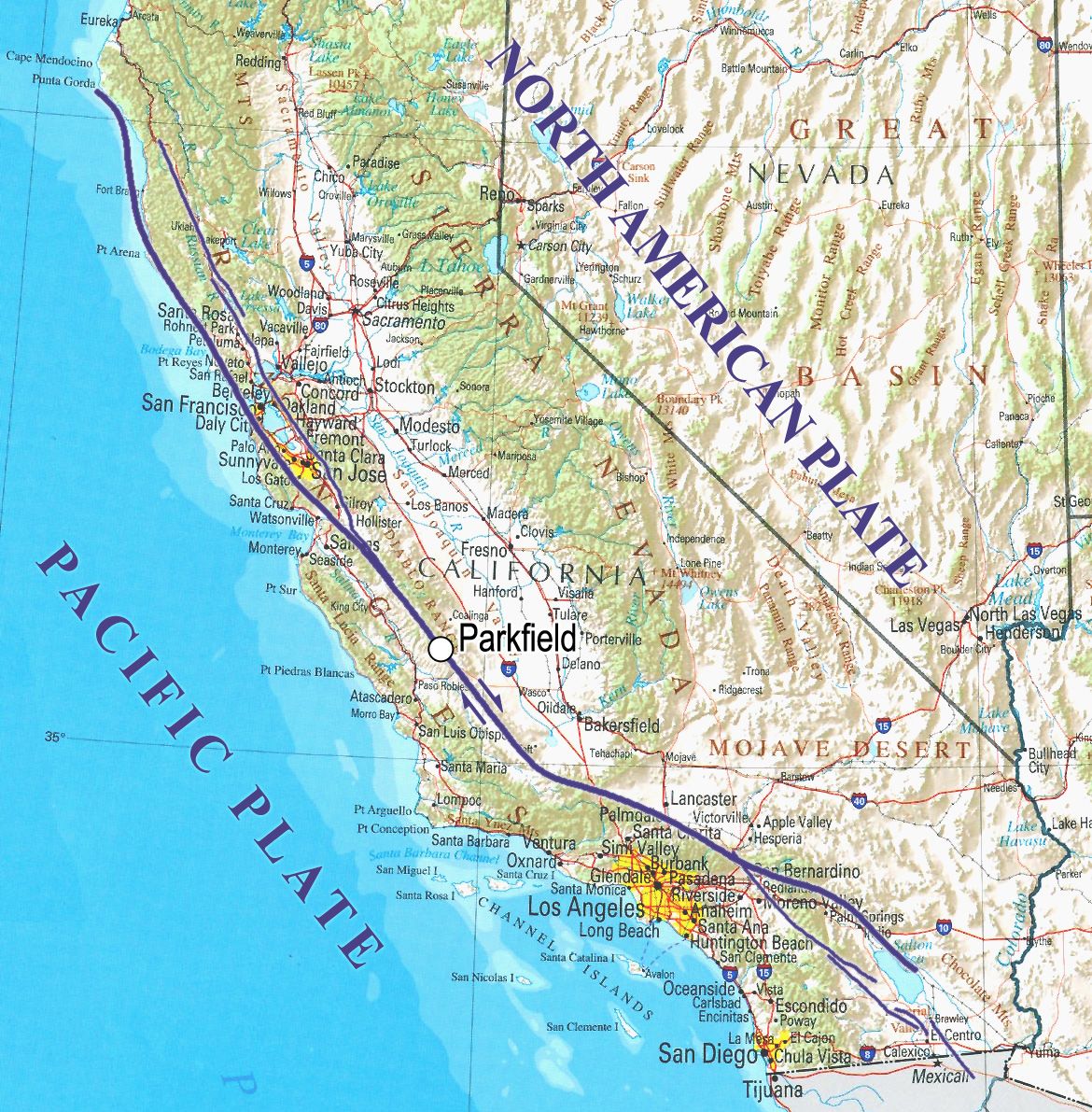
The Anatolian Fault is more than six times as deep as the San Andreas Fault
San Andreas Fault illustration
When it comes to depth, there is a clear winner between the Anatolian and San Andreas Faults. While the San Andreas Fault is as deep as ten miles in some places, the Anatolian Fault is as deep as a staggering 62 miles.
- San Andreas Fault maximum depth: 10 miles
- Anatolian Fault maximum depth: 62 miles
Of course, the most active parts of both faults are far shallower, with the most movement occurring in the Earth’s crust, versus the lower layers.
Neither the Anatolian nor San Andreas Fault has been fully and accurately mapped, largely due to the size and depth as well as limitations in access and technology.
Like the state of California, the country of Turkey lies atop a tectonic plate with a nearby fault line (the Anatolian Fault). However, Turkey also lies atop the Anatolian Plate, with the strike-slip activity between it and the Eurasian plate impacting large populations of people.

Related
Live Out Your “San Andreas” Fantasy On California’s Fault Line
The San Andreas Fault not only offers visitors to potentially experience an earthquake but to see the damage caused by one as well.
The fault also passes by Istanbul, which is Turkey’s largest city, one of the largest in Europe, and also the world’s most-visited city. In fact, the Anatolian Fault stretches for an impressively long distance, much farther than the San Andreas Fault.
Spanning 932 Miles, The Anatolian Fault Tops The San Andreas Fault
In contrast, the San Andreas Fault spans only 800 miles
Illustration of Anatolian plate and faults atop map of Turkey
What’s a hundred miles or so? A lot, when comparing jagged fault lines cutting through the Earth’s crust. In California, the San Andreas Fault spans around 800 miles, but in Turkey, the massive Anatolian Fault stretches about 932 miles.
- San Andreas Fault length: 800 miles
- Anatolian Fault length: 932 miles
- East Anatolian Fault length: 434 miles
However, that’s just the North Anatolian Fault’s length; another fault splits off and runs roughly East to West. The East Anatolian Fault is around 434 miles long on its own.
Turkey Has California Beat When It Comes To Earthquake Activity Along Its Fault Lines
California has a lot of earthquake activity, but Turkey has far more
Earthquake map for Turkey 1900 to 2023
Given that it is an entire country atop a tectonic plate, it’s not entirely surprising that Turkey experiences more earthquakes each year than California does. In fact, Turkey experiences more earthquakes per year than any other country, clocking in at around 74,000 earthquakes per year.
- Turkey experiences 74,000 earthquakes each year
- California experiences upwards of 10,000 earthquakes each year in Southern California alone
Of course, most of the earthquake activity around the world is hardly noticeable; an estimated 500,000 detectable earthquakes happen around the world each year, but only about 100,000 of those can be felt by people.
For Turkey, things might be changing, too. According to data from Statista, Turkey has experienced an increase in earthquake activity since the early 2000s. The country had 7,682 documented earthquakes in 2004, and that number more than tripled to 29,831 by 2011.
- To date, Turkey’s record for the most earthquakes in one year was in 2023, when the country had 74,232 earthquakes.
Given that both the Anatolian and San Andreas Faults are strike-slip faults, it’s not surprising that both geographical areas experience many earthquakes. However, other fault types—like reverse faults—can create much stronger earthquakes.

Related
These 12 Cities In Europe Attract The Most Tourists
Discover the enchanting cities of Europe, captivating travelers with their rich history, stunning architecture, and vibrant culture.
As for Turkey’s location atop the Anatolian Plate, the fault is a mere 12 miles away from Istanbul, and The Geological Society notes that the earthquake activity appears to be moving west. This could spell disaster for the city of Istanbul, which sustained heavy damage in 1999 even though the 7.6-magnitude earthquake’s epicenter was over 68 miles away.
California, on the other hand, has numerous cities that are vulnerable to earthquake activity—like San Francisco and Los Angeles—but none so large as Istanbul.
References: The Geological Society, California Residential Mitigation Program, Statista